How Much of Workers Work Does ChatGPT Do?
When ChatGPT hit the scene in late 2022, most workers had found a fancy tool that could write their emails for them. Over the past few years, usage has grown exponentially as employees started using it on their own for a much wider variety of tasks. They leaned on it to draft faster, debug code, brainstorm campaigns, and trim research time. Now, more than a quarter of U.S. workers are tapping ChatGPT on the job, and the rate climbs even higher among those with postgraduate degrees.
From Curiosity to Daily Habit
Personal use came first. Within months of launch, ChatGPT had already reached 100 million weekly active users, and that number has since surged to more than 700 million. Rather than waiting for IT to hand down approvals, employees imported their personal habits straight into work. Curiosity soon became routine. Surveys show 43% of U.S. knowledge workers now use AI, a leap from less than one in ten just two years ago. Pew reports that workplace use of ChatGPT alone grew from 8% in 2023 to 28% today.
This is not just a once-a-week check-in. More than half of those using AI at work rely on it four or more days each week, and daily use has doubled in the past year. The benefits are concrete. A Federal Reserve study found more than half of users save at least three hours a week, and Harvard research revealed a 40% bump in work quality among knowledge workers who use AI.
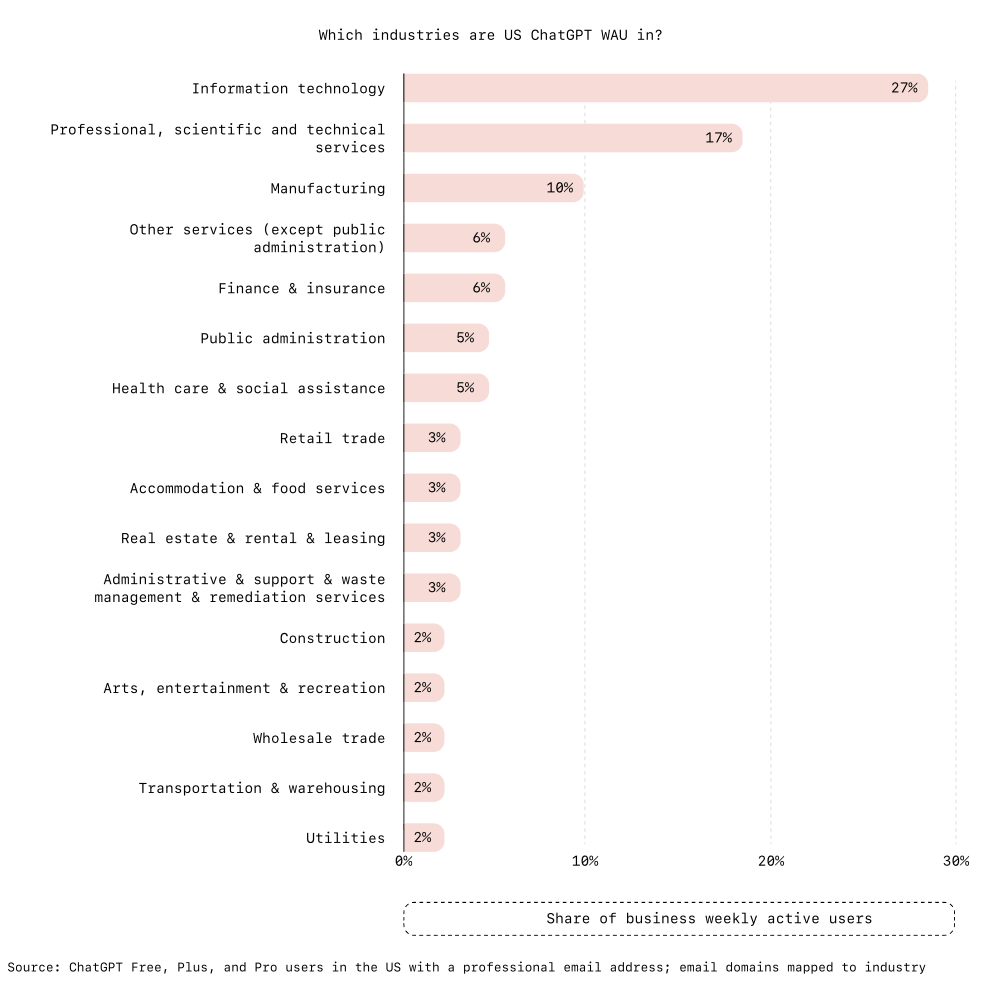
Industries at Different Speeds
Not every sector is moving at the same pace. Information technology leads the pack with 27% of U.S. ChatGPT weekly active users, followed by professional, scientific, and technical services at 17% and manufacturing at 10%. IT and finance lean heavily on coding and analysis, so their fast uptake is no surprise. Manufacturing’s adoption points to broader digital transformation, where AI supports supply chain improvements and process automation.
Other fields trail behind. Retail, construction, and agriculture see slower adoption, largely because they employ fewer knowledge workers. Healthcare is its own case. Despite being a data-intensive sector, regulatory strictness and risk aversion have slowed adoption. Even so, growth is showing up in specific areas such as clinical documentation.
How Different Teams Apply ChatGPT
During the first 90 days of use, four applications dominate: writing, research, programming, and analysis. Technical teams in analytics, engineering, and IT turn to ChatGPT for coding, troubleshooting, and planning. In contrast, marketing, sales, and communications teams lean on it for writing, research, creative ideas, and media generation. Across departments, the message is consistent: the tool is amplifying expertise rather than replacing it.
Engineers run prompts to refine code, analysts clean data, and support teams prepare customer-ready responses. Designers and product managers dip into coding assistance, while marketing teams brainstorm copy and campaigns. The result is that ChatGPT often serves as the starting point for work across the organization.
Everyday Tools vs. Advanced Features
For most employees, ChatGPT use centers on core features like search, data analysis, retrieval, and file uploads. Sophisticated functions such as custom instructions, deep research, and projects are still niche, with adoption concentrated in technical teams. Analytics, engineering, IT, and R&D roles rely more on advanced capabilities that fit their data-heavy workflows.
This uneven pattern creates both hurdles and openings. Advanced features remain underused, held back by discoverability issues and setup friction. As product design improves and training becomes more available, use will likely expand beyond quick productivity wins toward deeper reasoning and collaborative projects.
From Employee-Led to Enterprise-Driven
The workplace entry of ChatGPT turned the usual order on its head. Adoption started from the bottom up, with employees proving its value before leadership signed off. That bottom-up phase is now giving way to top-down integration. Companies are beginning to embed ChatGPT into departments, streamline operations, and rebuild processes with AI in mind.
Meanwhile, some professionals are using the tool at extraordinary levels. Segments of ChatGPT Pro subscribers send more than 200 messages a day, a sign of how deeply it can integrate into daily routines.
Looking Ahead
Work is shifting. Time once spent on basic communication or endless searching is being redirected toward synthesis, creativity, and quicker decision-making. Studies show AI reduces email time by nearly a third and gives developers more hours for exploration and coding. The payoff is not just higher output but a more satisfying work experience as repetitive tasks shrink.
Collaboration is changing as well. Teams are moving from static documents to real-time shared spaces. Features like memory and context awareness are turning ChatGPT into a personalized partner that adapts to each workflow.
The lesson for leaders is clear. Just as electricity revolutionized factories and the internet transformed communication, AI is ushering in a new era of productivity. Those who adopt early and invest in training will capture the biggest rewards, from faster decision-making to entirely new ways of operating.
ChatGPT and to a larger extent LLMs, are no longer just another productivity app. They are becoming the operating system for modern work. Leaders who act quickly and give their teams the skills to use it responsibly will unlock the greatest value and avoid being left behind by competitors already building AI fluency into their organizations.